The majority of people would rather watch films and television shows on a larger screen than on television. And now, since traveling to the movies is no longer an option, a projector is required to recreate the cinematic experience at home.
If you’re considering purchasing a projector, you should ensure that it supports keystone features, especially if you live in a small flat. Otherwise, your movie night may be a letdown.
On the other hand, the keystone projector is unknown to most people. Additionally, some are unaware of when and why they should utilize a keystone projector. Today, we will discuss what is keystone projector and why it should be used. Therefore, be sure to read to the end.

What is Keystone Projector?
A keystone projector is equipped with either manual or automatic keystone correction. When the projector is positioned on an inclined surface, a keystone occurs. You may adjust the projected image with a keystone projector to ensure an exactly aligned output.
Manual keystone correction is simply a physical modification to the projector’s lens to cause it to project at a different angle than it would on a flat surface. Although the manual adjustment is effective in some circumstances, it cannot completely eradicate horizontal keystone.
Automatic keystone adjustment is included with LCD and DLP projectors. When data is sent to the projector from an input device, it can be automatically transformed and scaled to compensate for the keystone effect.
This occurs when the projector’s scaling algorithm includes a selectable algorithm, which alters the image before reaching the projector lens. As a result, it is squared even if the image is viewed at an angle. Automatic keystone correction assists in ensuring a square image on the screen, even when the projector is angled.
Pros
- By adjusting the angles and forms of images via the digital settings, you can maintain the fixed position of the projector
- On the projector screen, obtain a rectangle image quality
- By correcting a distorted image, you can improve the overall output quality
- Adjust the projected image in accordance with the projector’s location
Cons
- The photographs presented may include digital distortions or have a lower resolution
Other Types of Keystone Correction
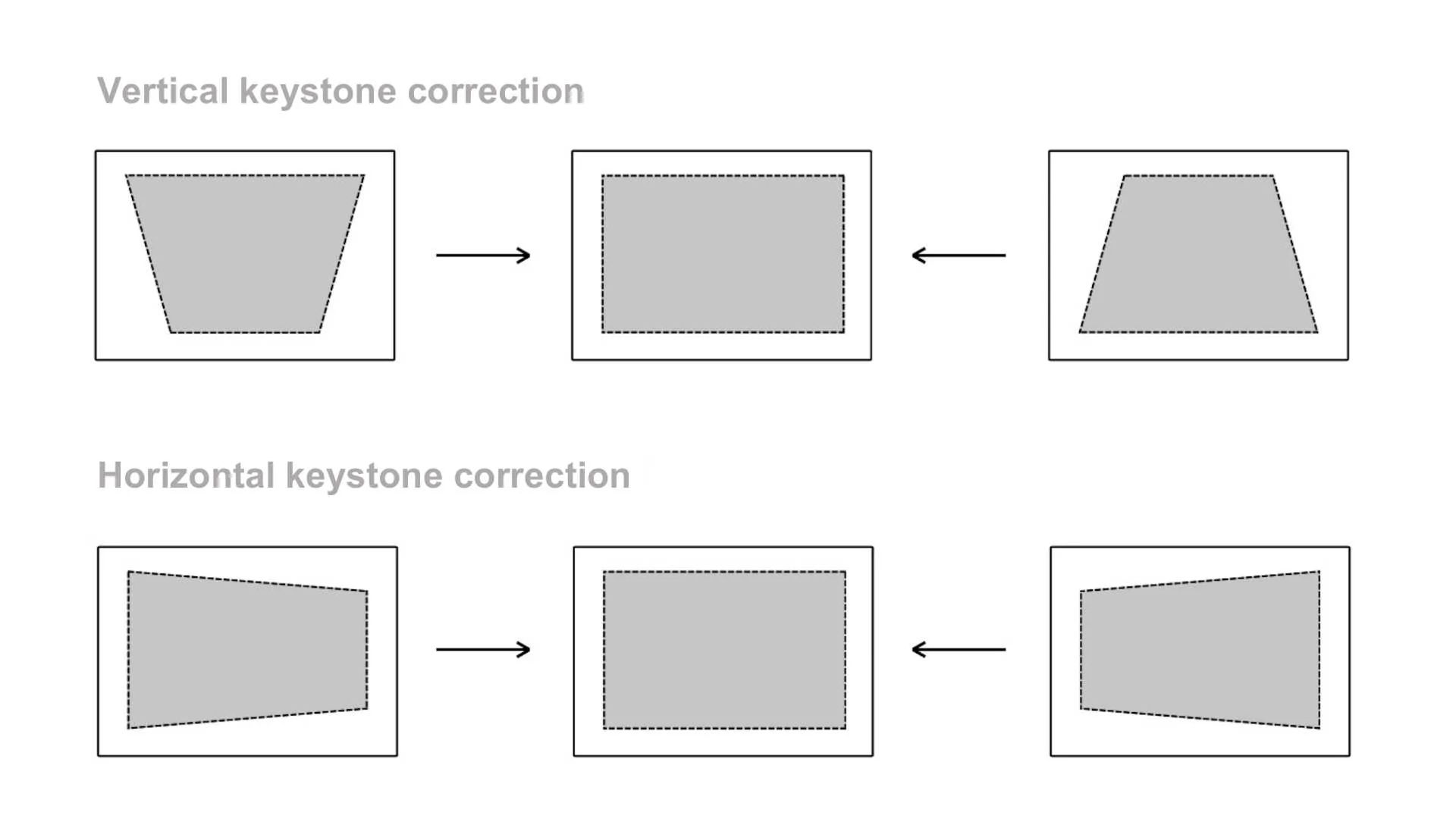
Vertical
Vertical keystone correction is used to repair an image that has been deformed from the top or bottom. If you encounter a distorted or misaligned image on the top or bottom, you must employ vertical keystone correction to obtain a rectangular image.
Horizontal
If the projector’s left or right side image is distorted, you must use the horizontal keystone adjustment option.
Related: What Is a 3D Projector?
How does Keystone Correction Work
Now that you know what is keystone projector and its type, let’s look at how it works.
Often, a projector cannot be placed directly in front of the screen. This gives the projection the appearance of a trapezoid rather than a rectangle. A keystone correction is an appropriate approach in this scenario. This tool enables you to alter the corners’ location.
The keystone correction mechanism is located on the top of most projectors. These buttons are sometimes also located on the remote control. The trapezoidal icon indicates which buttons are active. On the icon’s slenderest side, you’ll notice little arrows. When you touch the button, these arrows indicate which corners to change.
Rectify the corners
To apply horizontal and vertical keystone corrections, click the buttons. Continue until the image’s corners perfectly align with the screen’s corners. Typically, the projector displays a menu on which you may view all of the adjustments that have been performed. This way, you may easily restore the corners to their default configuration.
Keystone Correction VS Lens Shift
Without relocating the projector, lens shift and keystone correction allow you to modify the shape and positioning of the projected image. While most video projectors have keystone correction, most inexpensive projectors do not include lens shift as an option.
Lens shift enables you to physically move the lens assembly of the projector up, down, side-to-side, or diagonally without moving the projector. Keystone correction alters the image digitally before it passes through the lens. It is designed for use when the projector is not parallel to the screen, resulting in an uneven, trapezoidal image.
How to Correctly Adjust the Angle
Although digital angle correction has simplified the process significantly, many people still associate keystone correction with a frightening hassle. It may appear to be an additional barrier at first, but it’s something you’ll quickly adapt to, and once you do, it’ll become a convenient addition to your projectors.
Display your image
Naturally, the first step is to ascertain whether your image requires angle correction or not. You might have centered the projector from the start, avoiding the keystone effect altogether. However, this is a rare occurrence typically reserved for proper offices, auditoriums, and similar facilities. If you install one in your home, there is a strong possibility that the image presented may be deformed somehow.
Adjust the projector’s position
Although keystone angle correction aims to eliminate the manual labor associated with projector positioning, it is always preferable to place it in the center. This is because the less distortion in the image, the less degradation in the image following necessary angle corrections.
Self-distort the image
Keystone angle correction is a type of image distortion in which the output image’s angles are altered to seem rectangular to the audience. This can be accomplished by using the projector’s buttons. As the models differ, the functionality, button placements, and labeling of the buttons also vary.
However, virtually every projector today has angle distortion in vertical and horizontal orientations. If your image is too high or too low, or even extended on one side or the other, the buttons will guide you through the process of correction.
Read More: What Can I Use for a Projector Screen?
Increase or decrease the zoom level
To ensure that the output image fits precisely on your screen, you may also need to adjust the output image’s zoom level.
With these digital controls, you can make even the tiniest adjustments in front of you while seeing the output image without worrying about moving the projector excessively.